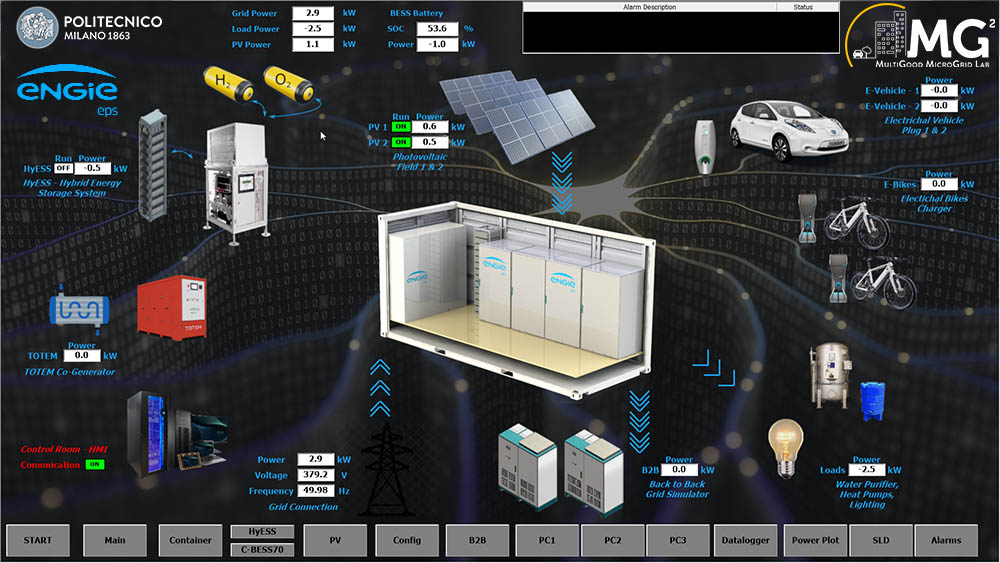
The MultiGood MicroGridLAB (MG2lab) is an experimental facility located in the Department of Energy buildings of Bovisa campus. It integrates various technologies for distributed energy generation and storage, constituting an active network that supplies heat, electricity, potable water and energy-related services together with electric vehicles, while minimizing operational cost.
Core mission of the MG2lab is the development and on-field testing of predictive optimization algorithms for optimal planning of multi-good energy systems, to ensure their secure and efficient operation also when featuring a high penetration of renewable generators.
MG2lab was built in collaboration with ENGIE-EPS.
The experimental rig features:
- Three photovoltaic fields installed on the roof of different campus buildings (total capacity 75 kW), a wind turbine and a micro CHP system;
- Programmable and non-programmable electric loads (water purifier, external lighting system, etc.);
- Electric and thermal storage systems;
- A reversible power-to-hydrogen system for long term energy storage;
- Charging stations for EVs;
- An electric grid simulator, possibly acting also as virtual electric load, to study islanded mode operation.
Grid Management
The flexibility of the MG2lab, and its diversified mix of distributed energy resources, allow to test on-field innovative solution for smart multi-energy management systems, and to compare with the major technical challenges that arise during the operation of real micro-grids.
The facility is involved in research activities that include:
Validation of optimisation algorithms for the solution of unit commitment, optimal power flow and predictive control problems accounting for load and renewables production forecast, and real-time monitoring. Objective of the optimisation is to minimise the operational cost, reduce renewables curtailment and increase renewables penetration.
Investigation of the characteristics and potential of distributed storage systems. The operation of different storage units is tested and modelled, to plan their utilisation both in islanded systems, as support for the optimal utilisation of available resources and real-time frequency and voltage control, and in grid-connected systems, to provide in addition market services. Moreover, research on hybrid hydrogen storage system, which can serve as a large capacity seasonal storage, is one of the main tasks of the MG2lab.
Optimal integration of EVs charging stations within microgrids. Charging stations do not behave as neat programmable loads, but can potentially offer variable degrees of demand-response. New strategies will be developed and tested, to dynamically optimise grid operations and transform EVs in revenue generating assets.